Your family, general, or pediatric dentist or orthodontist may refer you to an oral and maxillofacial surgeon for some dental treatments that require oral surgery. An oral surgeon is a specialist who has graduated from an accredited dental school and also completed additional education and residency related to surgical procedures needed to treat various oral diseases and conditions. An oral surgeon is trained in treating the following conditions:
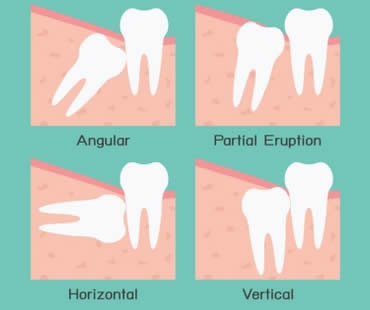
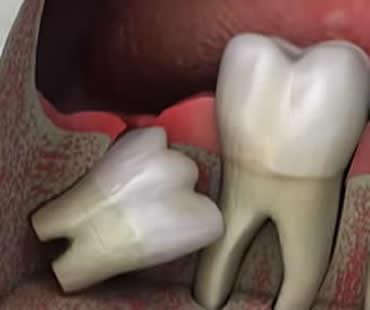
- Removal of diseased or impacted teeth
- Placement of dental implants
- Treatment of facial trauma involving gums, jaws, nasal cavities, cheekbones, eye sockets, and forehead
- Evaluation of pathologic conditions such as cysts and tumors of the mouth and face or acute infections of the oral cavity, salivary glands, neck, and jaws
- Treatment of facial pain including those caused by temporomandibular (TMJ) problems
- Cosmetic or reconstructive surgery to correct jaw, facial bone, and facial soft tissue problems
- Corrective jaw surgery
- Cleft lip and cleft palate repair
- Surgical treatment for sleep apnea
There are many different techniques that oral surgeons use to accomplish your treatment goals. The choice of techniques may vary between surgeons and should be discussed between you and your surgeon prior to the procedure.
Many oral surgery procedures can be completed in an outpatient setting. Often you are only in the office for a few hours and can return to your regular routine in a matter of days. A good oral surgeon will be able to perform these procedures with little chance of complications, and will be able to provide you with the information you need to understand the recovery process. Your oral surgeon will often collaborate with other specialists, such as an orthodontist or cosmetic dentist, to achieve your ultimate treatment goals.
If you live in the Weymouth area contact us today